Using Caché as an ODBC Data Source on Windows
This chapter describes how to perform a stand-alone ODBC installation under Windows, and how to create a DSN for a Caché database on Windows, which you can do either via the Control Panel or by creating a file DSN.
Performing a Stand-alone Installation
By default, Caché performs a full ODBC installation with a standard installation. If you perform a custom installation, you can select the “SQL client only” option to install only the client access components (ODBC client driver). For information, see the Caché Installation Guide.
In addition, however, Caché provides a simple stand-alone installer for Caché ODBC.
This installer is in the ODBC directory of the Caché DVD. This directory provides the following three files:
-
ODBCDriver_x86.exe will install 32-bit ODBC driver on any version of Windows.
-
ODBCDriver_ia64.exe can only be run on Windows 64-bit Itanium Edition and it will install 64-bit ODBC driver on this platform.
-
ODBCDriver_x64.exe can only be run on Windows x64 Edition and it will install 64-bit ODBC driver on this platform.
Run the installer that is appropriate for your platform and needs
Creating a DSN by Using the Control Panel
To create a DSN, you can use the Caché ODBC Data Source Setup dialog box. To access this dialog box, click the ODBC Data Sources icon, either in Windows Control Panel or its Administrative Tools subpanel. On the User DSN tab, click the Add... button, select Intersystems ODBC, and click the Finish button. The dialog box looks like the following example:
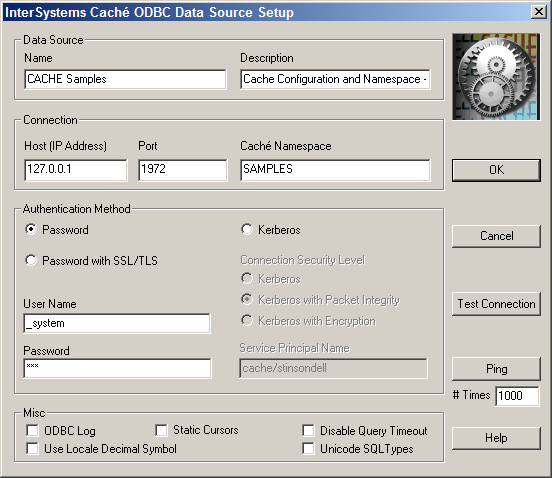
Use this dialog box to specify the details for a specific Caché ODBC data source. The fields are listed below and are required unless otherwise specified:
-
Name — Specifies the name of the DSN.
-
Description — Specifies an optional description of the DSN.
-
Host IP Address — Specifies the IP address of the DSN in dotted decimal or dotted quad form, such as “127.0.0.1”.
-
Host Port Number — Specifies the port for connecting to the DSN. The default for Caché is 1972.
-
Caché Namespace — Specifies the namespace for the DSN.
-
Authentication Method — Select either Password or Kerberos, depending on the security used for this database.
If you select Kerberos, also specify the following additional settings:
-
Connection Security Level — Select Kerberos, Kerberos with Packet Integrity, or Kerberos with Encryption, as appropriate.
-
Service Principal Name — Specify the name of the service principal that represents Caché.
For more information on Kerberos, see the Caché Security Administration Guide.
-
-
User Name — Optionally specifies the username for logging into the DSN. By default, this is “_SYSTEM” and is not case-sensitive.
-
Password — Optionally specifies the password for the account specified by the UID entry. For the SYSTEM username, the password is “SYS” and is case-sensitive.
-
ODBC Log — If selected, specifies the creation of a log file of ODBC client driver activities for all Caché DSNs. This log is for troubleshooting; you should not turn logging on during normal operation as it will dramatically slow down ODBC performance. See the chapter on “Logging” for more information.
-
Static Cursors — If selected, enables the Caché ODBC client driver’s static cursor support. If this flag is off, then the cursor support provided by the ODBC Cursor Library will be used. In general, this flag should be off unless you have a specific reason for not using the ODBC Cursor Library.
-
Disable Query Timeout — If selected, causes the ODBC client driver to ignore the value of the ODBC query timeout setting.
The ODBC query timeout setting specifies how long a client should wait for a specific operation to finish. If an operation does not finish within the specified time, it is automatically cancelled. The ODBC API provides functions to set this timeout value programmatically. Some ODBC applications, however, hard-code this value. If you are using an ODBC application that does not allow you to set the timeout value and the timeout value is too small, you can use the Disable Query Timeout option to disable timeouts.
-
Use Locale Decimal Symbol — When selected, specifies the use of the current locale's decimal separator; not checking this sets the decimal separator in the process to a period (".") regardless of the locale. This value can have an affect when the ODBC connection is interoperating with an application that uses the decimal separator as defined for the current locale.
-
Unicode SQL Types — If selected, turns on reporting of a Unicode SQL type (“SQL_WVARCHAR (-9) SQLType”) for string data. This allows Microsoft Office 2000 and Visual Basic applications to allocate the properly sized buffers to hold multibyte data. This functionality is only relevant if you are working with a multibyte character set, such as in Chinese, Hebrew, Japanese, or Korean locales. If you are only using single-byte character set data, do not select this check box.
If an application encounters a “SQL data type out of range” error from the Microsoft Driver Manager using SQLBindParameter, it can be caused by having selected this check box.
After you have created the DSN, you can use the Test Connection button to see if your data source is working correctly.
On Windows 64-bit, use the Windows Control Panel ODBC Administrator to create user DSNs that function for both 32- and 64-bit programs. To configure a system DSN for a 32-bit program, run %SystemRoot%\SysWow64\odbcad32.exe.
Creating a File DSN
Caché also supports file DSNs. A file DSN is a normal file that contains information to establish a connection via ODBC. Additional information can be found on the Microsoft support siteOpens in a new tab (search on "file DSN").
The connection specifies the file to use:
filedsn=<fully qualified path for the DSN>
A file DSN is invoked via SQLDriverConnect where you specify the file DSN. It can specify an existing DSN to use, for example,
[ODBC]
DSN=CACHE Samples
or specify the full set of connection parameters
DRIVER=InterSystems ODBC
SERVER=127.0.0.1
PORT=1972
DATABASE=SAMPLES
AUTHENTICATION METHOD=0
QUERY TIMEOUT=1
UID=_system
PWD=SYS
If the user ID or password is not supplied as part of the connection parameters, the connection manager will prompt for them.
Commonly used file DSNs are usually stored in the following directory:
%SystemRoot%\Program Files\Common Files\ODBC\Data Sources